Sometimes the things can go wrong even for the best of us. Let’s suppose we have a reputed antivirus, an antispyware as a complementary security tool and a firewall installed in the PC, we keep the system and these programs always up-to date. Despite all of our efforts to stay away from troubles, we just get infected with a trojan virus.
The golden rule is to periodically scan your computer with an up to date antivirus which theoretically will get rid of any trojan virus but always will work this method ? An antivirus can not alert us in the case of an infection with an unknown or very new trojan virus, therefore it’s not recommended to rely only on protection provided by the antivirus software, it is a good idea to use other methods of detection from time to time, but which are these alternative methods ? How can we know our computer is infected ?
There are a few symptoms indicating the presence of a trojan in our PC but keep in mind please, that if none of these are present, that’s not mean the operating system is in a necessary mode clean: the virus creators make great efforts to create trojans with a very low impact on the performances of the infected systems, one of the main goals in programming a trojan virus is to hide its presence, to run it on victim’s computer as unnoticed as possible. The truth is, since a virus trojan run at the level of a computer administrator, the infected computer behaviour is determined by the attacker, so it’s very hard to enumerate specific symptoms of a trojan virus infection.
Generally speaking, the presence of a trojan can be indicated by :
– the change of your browser homepage;
– certain programs suddenly shut down or start without user intervention;
– new files or text messages appears on the desktop, strange sounds can be heard, the mouse has a strange behaviour, the background is changed, the computer shut down or restart without user intervention but these are very rare cases, unless the attacker is a kid playing his jokes on the victims nerves;
– the Task Manager or the Registry Editor become inaccessible;
– the browsing speed become very slow;
– the antivirus is disabled without an apparent reason or the antivirus can not be updated anymore;
– you are not able to install a certain antivirus or antimalware program;
– a large amount of advertising pop-ups while surfing the Internet;
– frequent logouts in the middle of an online banking transaction. A trojan can cause logouts to force the victim to reintroduce the login credentials and steal them(keylogging);
– indirect signs of a trojan activity can be found in the user online accounts. For example your friends receive emails apparently from you but you don’t sent them. Or, in an email inbox the unread emails looks different than the read ones. The read emails can be presented with an open envelope like icon, if you know you don’t have read the emails, that’s a sign that somebody else read them. In a lot of online banking accounts dashboard there is presented the last IP logged into the account, take note of this and compare with your IP, see if they are matching. This is simple if you have a static IP, but if you have a dynamic IP (DSL or dial-up connection), note somewhere the IP used when you do online transactions. To find your IP visit www.whatismyip.com
– you can’t navigate to certain websites, you are redirected to other site than the wished one;
– your search results looks strange, with a lot of advertisements — the search results are hacked;
– Very Important ! A browser process running but without the browser being opened really. For example, we can see in the Task Manager any of these executables running as processes: iexplorer.exe, firefox.exe, opera.exe, YahooMessenger.exe, but we have not opened them and we can not see their windows. These processes simply are running silently without a window, like a ghost: that’s a strong sign of a trojan infection, they very often inject their code into legitimate processes memory space, in order to deceive the antivirus detection. Also a browser process requesting access to the Internet will not raise suspicions. Other case is when we can see multiple instances of the same browser running, but only one is opened by us — it’s not sure this is a sign of an infection because a browser can open multiple instances by itself, but we must investigate each browser process.
There are three zones where a virus trojan can be unveiled: the running processes, the autostart items and the network connections . I have used a well known trojan virus(in fact is a Remote Administration Tool, how the author like to name it, it’s publicly available on the Internet) to infect my own computer and to perform some tests.
This is how an “infected” browser process are looking in Process Hacker, a simple but powerful program:

As you can see in the above image, there are two Opera browser processes running, one legitimate and consuming a large amount of RAM memory(192,3MB, that’s normal) and one process infected consuming only 1MB – very unusual. More important, the window information tab is grey that’s mean deactivated, the informations about a window associated with the process are missing. A browser without a window, very strange, isn’t it ? It seems it is started in console mode.
The real Opera browser process has a window and Process Hacker can deal with it:
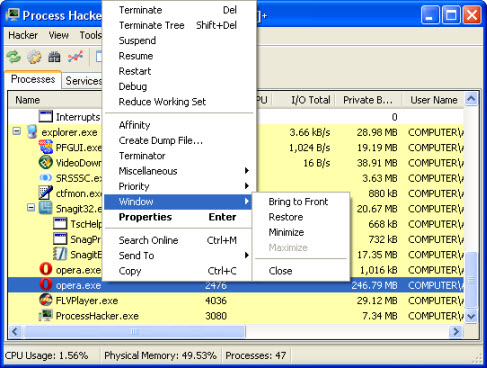
Very important to mention, the fake Opera process, the infected one is always in wait:suspended state and threads associated with it are only two :
–opera.exe in wait:suspended state;
–kernel32.dll! CreateThread+0x22(this is the start adress) necessary for the trojan to create its own thread inside the Opera host process. This thread is in wait:DelayExecution state;
In contradiction with this behaviour, the legitimate Opera process open a lot more threads, in my tests nine threads all active–no suspended threads. Searching for strings in private regions of the memory allocated to the infected process(in right-click menu go to Properties>Memory>Strings and tick Detect Unicode and Private for the memory regions also set the Minimum Length of the strings to 4) will reveal the location of the virus trojan file, the name of it, the domain or IP adress where it connects, the registry key used for autostart, the nickname which the attacker gives to the trojan to identify it, pretty much all the informations you need to get rid of it. Even if the trojan virus is in an encrypted form on hard disk, it will be automatically decrypted in RAM memory.
All these may to look a bit complicated but Process Hacker is a very friendly program and after playing a little with it, you will learn everything about it. It is very similar to Sysinternals Process Explorer . It is true that you must be a bit skilled, to know at least what a process, a thread or what computer RAM memory is. But, investigating your computer is a source of a lot of fun.
The attacker, at the creation time of the virus trojan has a few options, in which process to inject it, the most used are the default browser, explorer.exe, services.exe and svchost.exe because these processes can be found in any computer running Microsoft Windows. Also the attacker can choose in which directory the trojan will be dropped: system32, temporary(temp) directory, Application Data, AppData, Roaming and so on.
Let’s enumerate the main features of trojan viruses :
– they can inject themselves into a legitimate process;
– they add a registry entry for autostart;
– they uses reverse connections to deceive the firewalls;
– they infect computers in an encrypted form. Hackers use very often executables crypters to bypass the signature based antivirus detection and the trojan will be decrypted in the RAM memory, where the antiviruses are not so effective. This way, a public available virus trojan can have a million different signatures some of them undetectable. If the trojan is very new and carefully crypted, an antivirus will not recognize it, even heuristically.
A reverse connection very often used by the common virus trojans, is a connection where the trojan virus will open a port on the infected computer and will send a SYN packet to an IP or domain embedded by the attacker in the trojan body at the creation time. This IP or domain is where the attacker listen for victim’s SYN packets and once they are received, he will respond to them establishing a connection, but as you can see the connection is initiated by the trojan virus or a firewall will block by default the inbound traffic, not the outbound one. In conclusion, the trojan’s communications with the command & Control server are able to bypass the firewall.
It is like the trojan open the door from within the infected computer and invites the attacker inside. Because the door was opened from inside, the firewall will not consider the attacker as a thief and will not block him.
In the Network tab of the Process Hacker, can be seen how the trojan virus send once at each 20 seconds the SYN packet, looking for a connection to the attacker’s PC. If the trojan Command and Control server installed in the hacker PC will respond to these messages, then the connection state will be changed to Established.
Autoruns is a very useful program to determine what kind of autostart a trojan virus uses. Let’s see this, in our test :
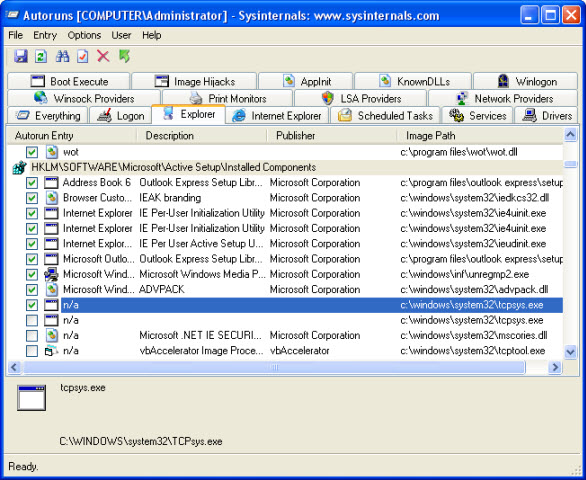
Here the trojan virus uses the Active X startup method. There are several registry locations used by trojans for autostart, the most used are:
– HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
– HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunOnce
– HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
– HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunOnce
– Active X method. The autostart is achieved by creating a new key under HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Active Setup\Installed Components with a random name. After computer boot, other key is created by the system : HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Active Setup\Installed Components with the same random name as the previous one. As long as this second key sit there in the registry, the trojan will not start at boot time, but the trojan is clever enough to delete this second key each time he’s running, assuring its autostart at next boot.
To be sure that a trojan virus will not run at computer start-up, it’s enough to delete the first registry key : HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Active Setup\Installed Components\RANDOM_NAME
We can see in the above image, the Active X autostart used for a trojan virus located in system32 folder with the name tcpsys.exe. Now, to get rid of this trojan virus, is enough to delete it from system32 folder.
It’s recommended to be used Unlocker program, it can unlock and delete files or will delete them at the first computer restart if the files can not be unlocked, this way will be avoided deleting errors.
The method exposed here to get rid of a trojan virus works for the most common trojan viruses as : Bifrost, Poison Ivy, SpyNet, CyberGate and others aswell. However, if you feel uncomfortable editing the registry or if you find the methods described here as complicated, although them are not at all difficult to understand, it’s recommended to scan periodically your system with a well reputed professional Antivirus or Internet Security Suite as:
I found these products as the most effective at getting rid of a trojan virus, other antivirus or antimalware solutions can perform well also, but it’s not recommended to test on yourself all the new security products on the market if you are serious about your computer security, take the time and read carefully the reviews before to purchase any of them.
Keep safe !





Leave a Reply